What is Net Ecosystem Exchange (NEE)?
By Ellen Young
August 29th, 2024
Data provides the first layer of defense in the fight against climate change. Without accurate data, corporations, governments, and individuals alike cannot effectively plan and execute interventions that will mitigate the worst impacts of climate change and allow for compliance and operational excellence.
But, not all data is created equally, and traditional methods that involve manual sampling of individual carbon pools will soon be obsolete. CarbonSpace measures climate change where it happens—directly in the atmosphere—to understand an ecosystem's carbon composition.
But, not all data is created equally, and traditional methods that involve manual sampling of individual carbon pools will soon be obsolete. CarbonSpace measures climate change where it happens—directly in the atmosphere—to understand an ecosystem's carbon composition.
Direct, ecosystem-level carbon measurement unlocks more accurate carbon footprint calculations, enabling businesses to identify and reduce emissions hotspots in their supply chains.
We call this ecosystem-level measurement “Net Ecosystem Exchange,” or “NEE.” In this guide, we’ll cover the basics of what NEE means, how it works, and its potential to transform carbon management for land-based activities like agriculture and forestry.
We call this ecosystem-level measurement “Net Ecosystem Exchange,” or “NEE.” In this guide, we’ll cover the basics of what NEE means, how it works, and its potential to transform carbon management for land-based activities like agriculture and forestry.
What is NEE?
Net Ecosystem Exchange (NEE) is a measure of the balance between carbon dioxide (CO2) absorbed by an ecosystem (sequestration) and CO2 released from an ecosystem (emissions). It's a snapshot of an ecosystem's carbon footprint. Understanding NEE is crucial for tracking carbon sequestration and emissions, especially in land-based activities like agriculture and forestry.
CarbonSpace's methodology for monitoring NEE is third-party verified and fully compatible with the GHG Protocol’s flow and stock change carbon accounting methods, among other leading industry standards.
What is included in NEE?
Plants absorb CO2 from the atmosphere through photosynthesis to produce energy and grow. Conversely, all living organisms, including plants, release CO2 through respiration. NEE is the net result of these opposing processes.
Calculating NEE is complex because various factors influence photosynthesis and respiration rates, such as land cover type, region, weather conditions, and land management practices.
Why does NEE matter?
Climate change happens in the atmosphere, yet corporations and carbon credits today use biomass-based measurements and outdated industry averages to measure efforts and demonstrate progress.
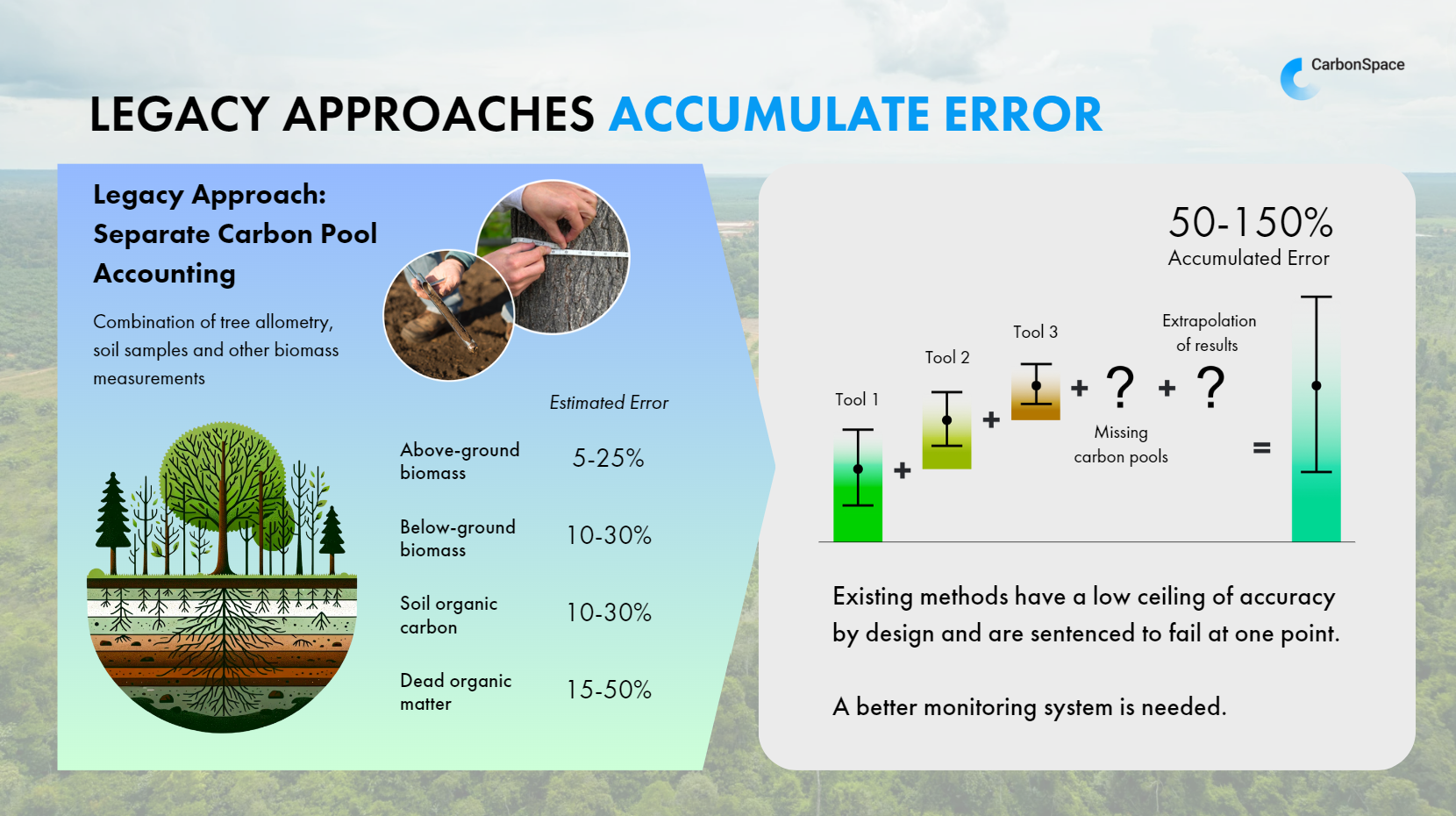
Mainstream methods today measure only individual carbon pools like soil or above-ground biomass. Companies miss out on additional, essential carbon pools and accumulate 50-150% uncertainty due to less accurate sampling methods and technology. Plus, sampling inherits human bias and other sources of errors, and can even open the door to potential greenwashing. Greenwashing and lack of data standards lead to the need for sustainable models and changes.
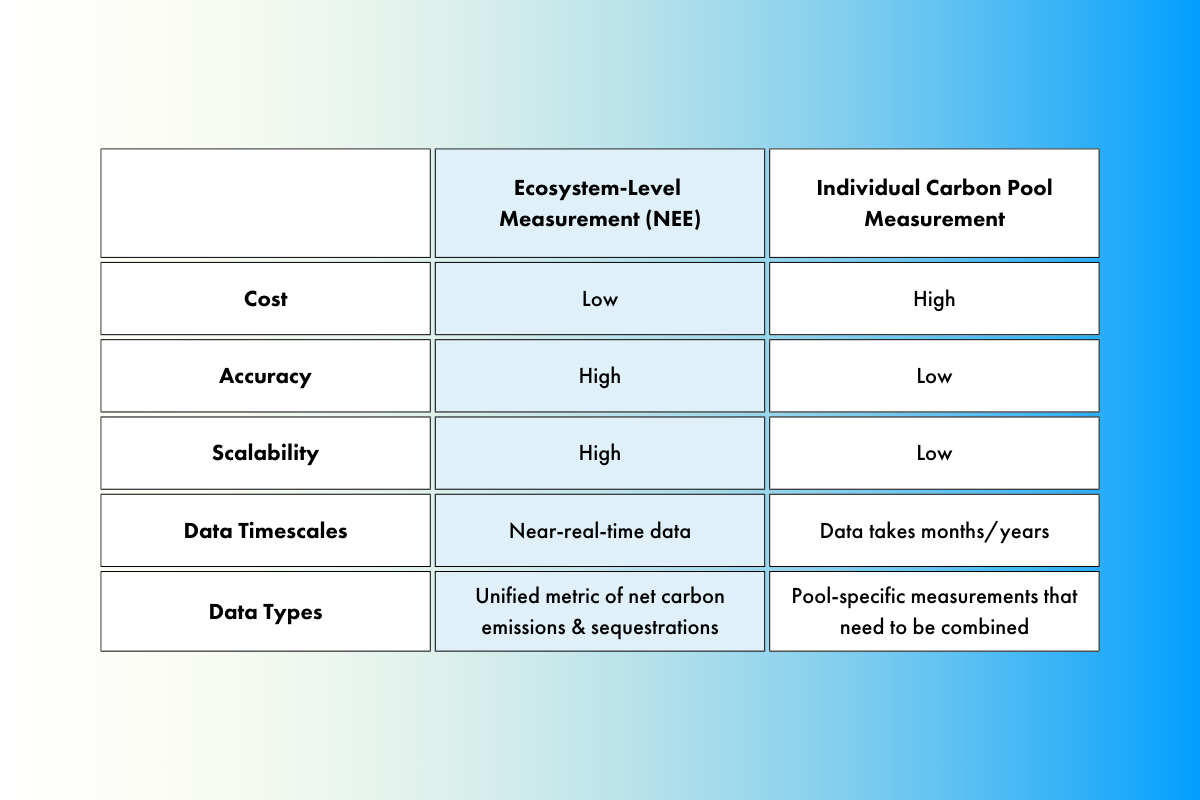
NEE is an atmospheric measurement that offers a comprehensive view of an ecosystem's carbon dynamics compared to traditional methods. NEE provides a holistic picture of an ecosystem's health and productivity by considering all carbon pools (aboveground and belowground biomass, soil, and dead organic matter).
This makes NEE valuable for:
Net Ecosystem Exchange (NEE) is a measure of the balance between carbon dioxide (CO2) absorbed by an ecosystem (sequestration) and CO2 released from an ecosystem (emissions). It's a snapshot of an ecosystem's carbon footprint. Understanding NEE is crucial for tracking carbon sequestration and emissions, especially in land-based activities like agriculture and forestry.
CarbonSpace's methodology for monitoring NEE is third-party verified and fully compatible with the GHG Protocol’s flow and stock change carbon accounting methods, among other leading industry standards.
What is included in NEE?
Plants absorb CO2 from the atmosphere through photosynthesis to produce energy and grow. Conversely, all living organisms, including plants, release CO2 through respiration. NEE is the net result of these opposing processes.
Calculating NEE is complex because various factors influence photosynthesis and respiration rates, such as land cover type, region, weather conditions, and land management practices.
Why does NEE matter?
Climate change happens in the atmosphere, yet corporations and carbon credits today use biomass-based measurements and outdated industry averages to measure efforts and demonstrate progress.
Mainstream methods today measure only individual carbon pools like soil or above-ground biomass. Companies miss out on additional, essential carbon pools and accumulate 50-150% uncertainty due to less accurate sampling methods and technology. Plus, sampling inherits human bias and other sources of errors, and can even open the door to potential greenwashing. Greenwashing and lack of data standards lead to the need for sustainable models and changes.
NEE is an atmospheric measurement that offers a comprehensive view of an ecosystem's carbon dynamics compared to traditional methods. NEE provides a holistic picture of an ecosystem's health and productivity by considering all carbon pools (aboveground and belowground biomass, soil, and dead organic matter).
This makes NEE valuable for:
- Assessing carbon sequestration potential: Areas with a negative NEE actively remove carbon from the atmosphere.
- Monitoring land-use impacts: NEE can track the carbon footprint of different land management practices.
- Informing climate mitigation strategies: Understanding NEE helps identify opportunities for carbon sequestration and emission reductions.
- And more.
How is NEE measured?
Accurately measuring NEE requires advanced techniques. The eddy-covariance method is a standard approach that directly, precisely, and continuously determines the CO2 and water vapor flows of an ecosystem. It is the most efficient way we have today to measure the interactions between a terrestrial biosphere and the atmosphere on an ecological scale (Friend et al., 2006; Baldocchi, 2008). However, deploying and maintaining eddy covariance towers is costly and impractical for large-scale monitoring.
CarbonSpace has developed a method to overcome these challenges by combining satellite imagery with direct, eddy-covariance measurements. This enables NEE estimates across vast areas, making carbon flux tracking more accessible, cost-efficient, and scalable.
What are the benefits of NEE?
NEE offers several advantages over traditional carbon monitoring methods:
- Comprehensive: Accounts for all carbon pools and processes.
- Accurate: Leverages advanced measurement techniques and data analysis.
- Scalable: Can be applied to large areas through remote sensing.
- Actionable: Provides insights for improving land management and reducing carbon footprints.
By accurately measuring the balance between carbon uptake and release, NEE provides valuable insights to enable businesses to remain compliant and competitive. Understanding and managing carbon emissions is vital for risk mitigation, competitive advantage, regulatory compliance, efficiency, and more.
As the world transitions to a low-carbon future, embracing NEE as a key metric will be instrumental in achieving climate goals based on directly measured, actual ecosystem performance. CarbonSpace is at the forefront of NEE monitoring technology, offering a robust and scalable platform to support organizations in reaching their climate goals.
As the world transitions to a low-carbon future, embracing NEE as a key metric will be instrumental in achieving climate goals based on directly measured, actual ecosystem performance. CarbonSpace is at the forefront of NEE monitoring technology, offering a robust and scalable platform to support organizations in reaching their climate goals.

